 RLLM Serving
RLLM Serving
The reasoning large language model (RLLM) has been proven competitive in solving complex reasoning tasks such as mathematics, coding, compared to general LLM. However, the serving performance and behavior of RLLM remains unexplored, which may undermine the deployment and utilization of RLLM in real-world scenario. To close this gap, in this paper, we conduct a comprehensive study of RLLM service. We first perform a pilot study on comparing the serving performance between RLLM and traditional LLM and reveal that there are several distinct differences regarding serving behavior: (1) significant memory usage and fluctuations; (2) straggler requests; (3) adaptive running time; (4) domain preference. Then we further investigate whether existing inference optimization techniques are valid for RLLM. Our main takeaways are that model quantization methods and speculative decoding can improve service system efficiency with a small compromise to RLLM accuracy, while prefix caching, KV cache quantization may even degrade accuracy or serving performance for small RLLM. Lastly, we conductevaluation under real world workload modeled by Gamma distribution to verify our findings. Empirical results for real world workload evaluation across different dataset are aligned with our main findings regarding RLLM serving. We hope our work can provide the research community and industry with insights to advance RLLM inference serving.
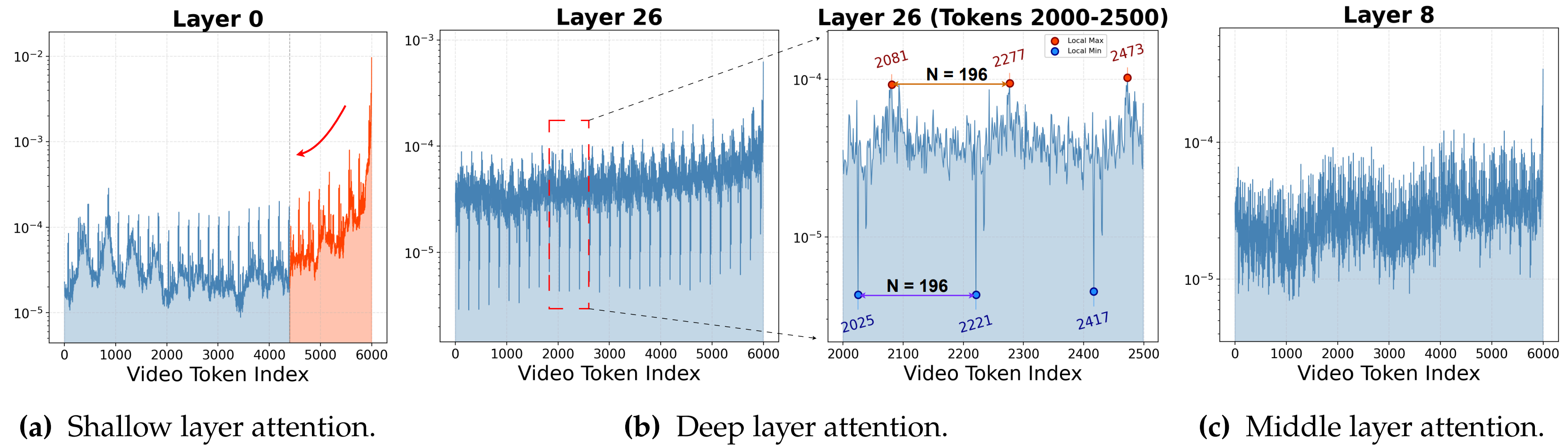
Visualization of the average attention weights (log scale) for user queries over video tokens in \llava with a FIFO KV cache budget of 6K video tokens per layer, averaged across 300 user video questions.
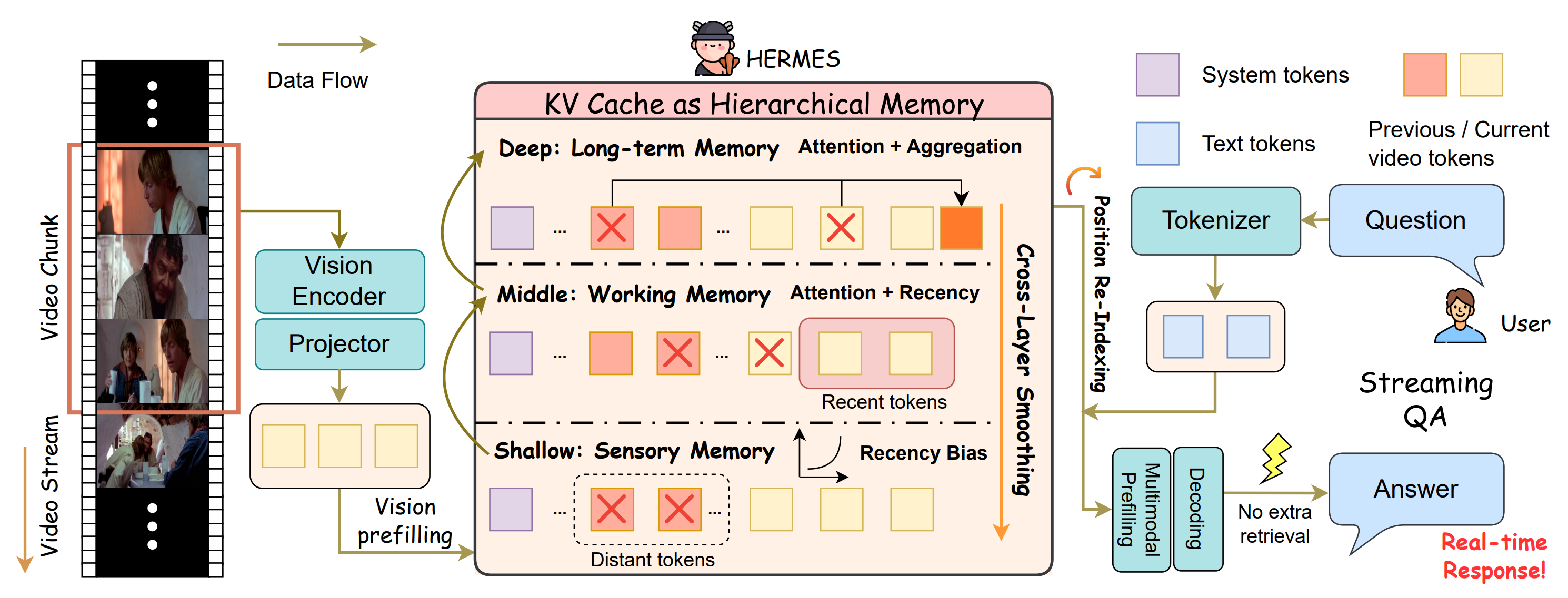
Overview of the HERMES architecture for streaming video QA. By implementing a hierarchical KV cache and specialized management strategies, HERMES enables real-time and accurate responses through direct cache reuse, eliminating the need for additional retrieval operations or external memory whenever users pose questions.
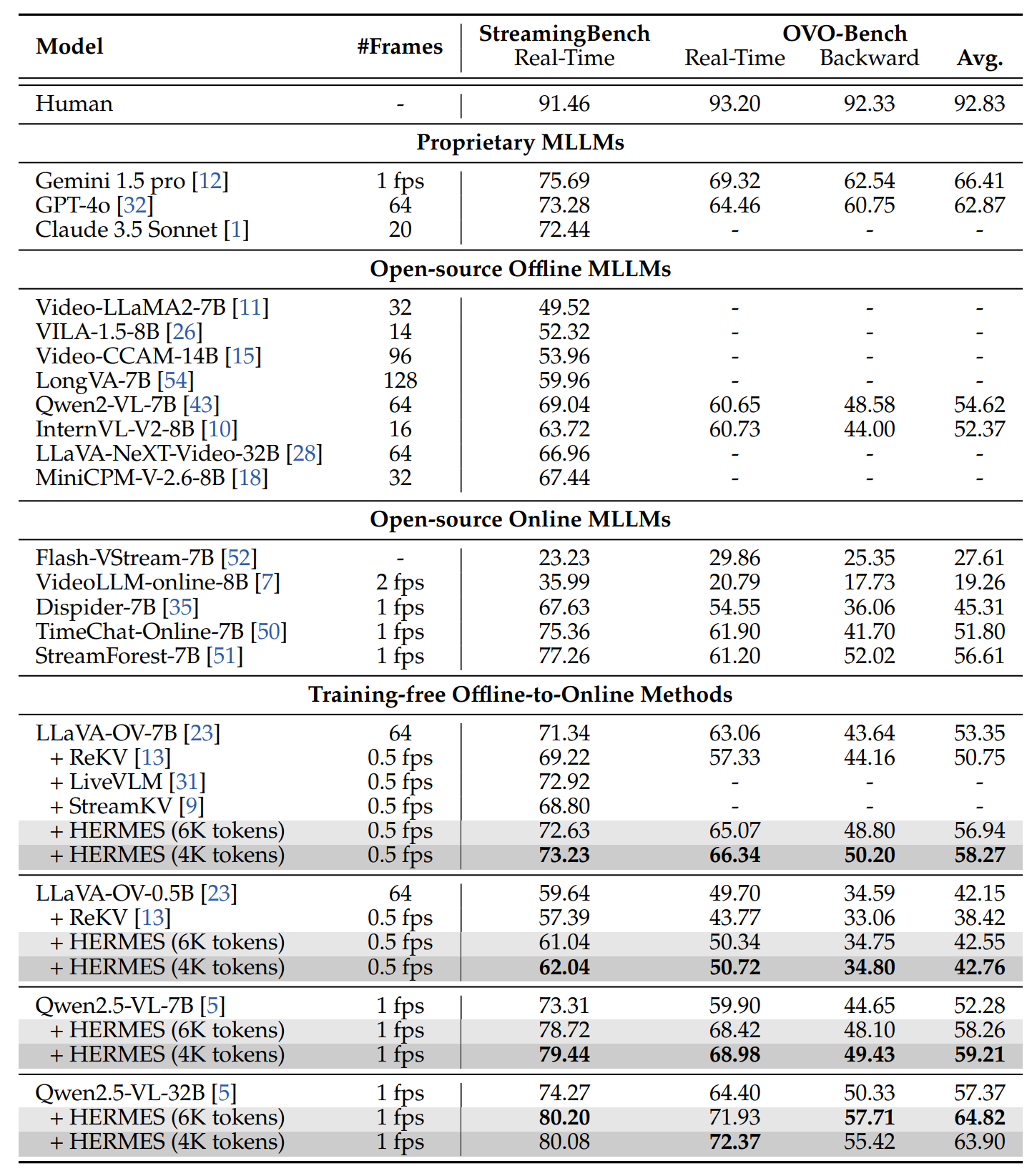
Performance comparison (%) on StreamingBench and OVO-Bench. The "Avg." column reports the results of the average accuracy of real-time visual perception and backward tracing tasks.
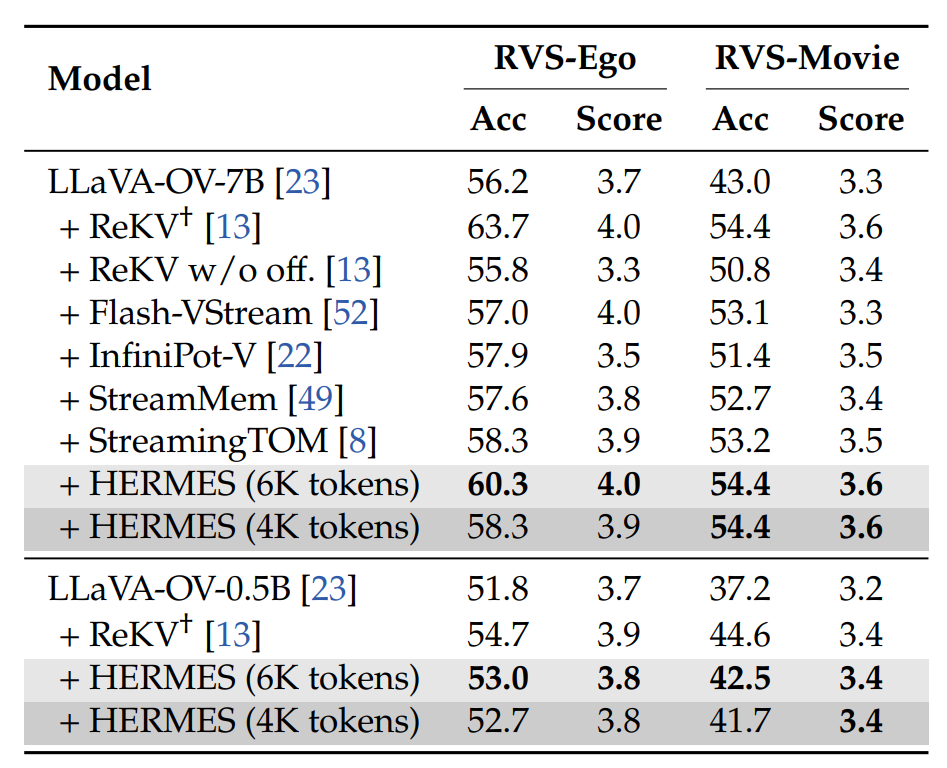
Performance on RVS-Ego and RVS-Movie. †: ReKV caches the KV states of all previously seen frames and is therefore treated as an upper bound.
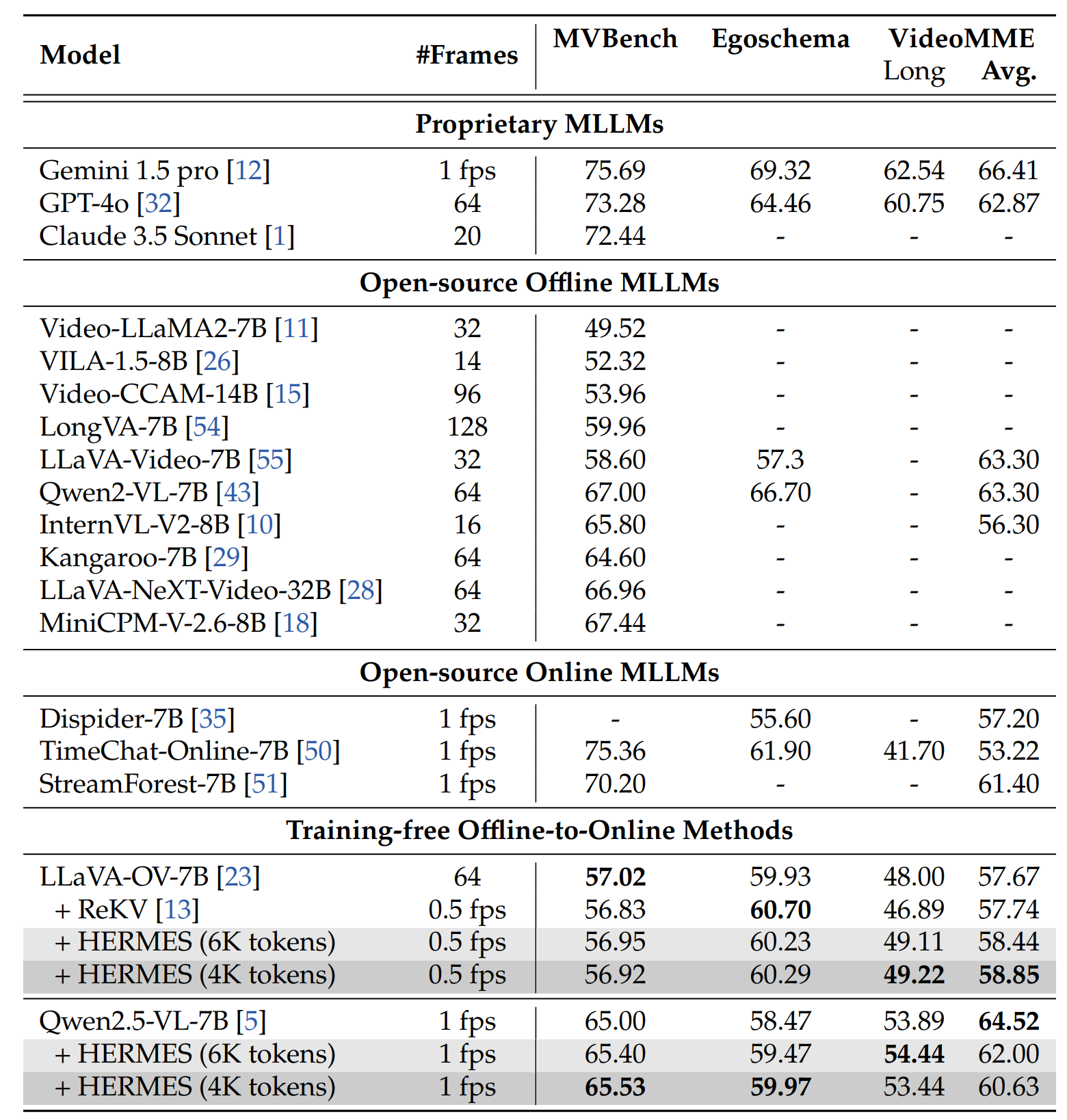
Performance comparison (%) on offline benchmarks.
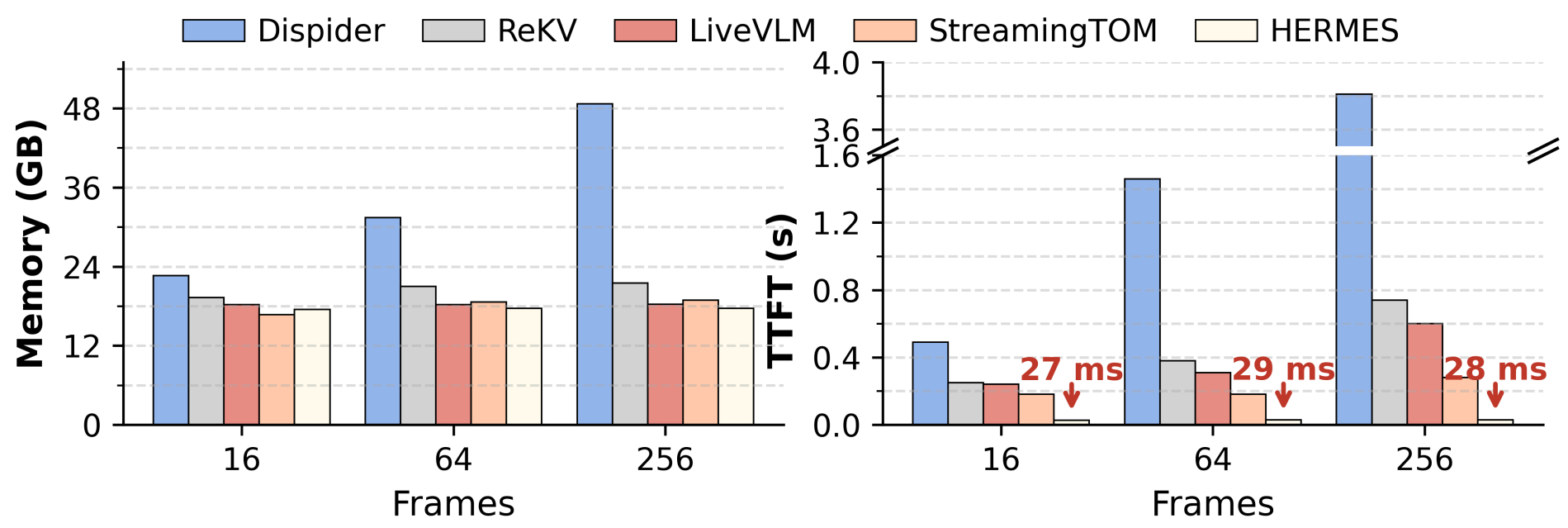
GPU memory and TTFT latency comparison across input frame numbers. HERMES achieves 10× faster in TTFT compared to prior SOTA.
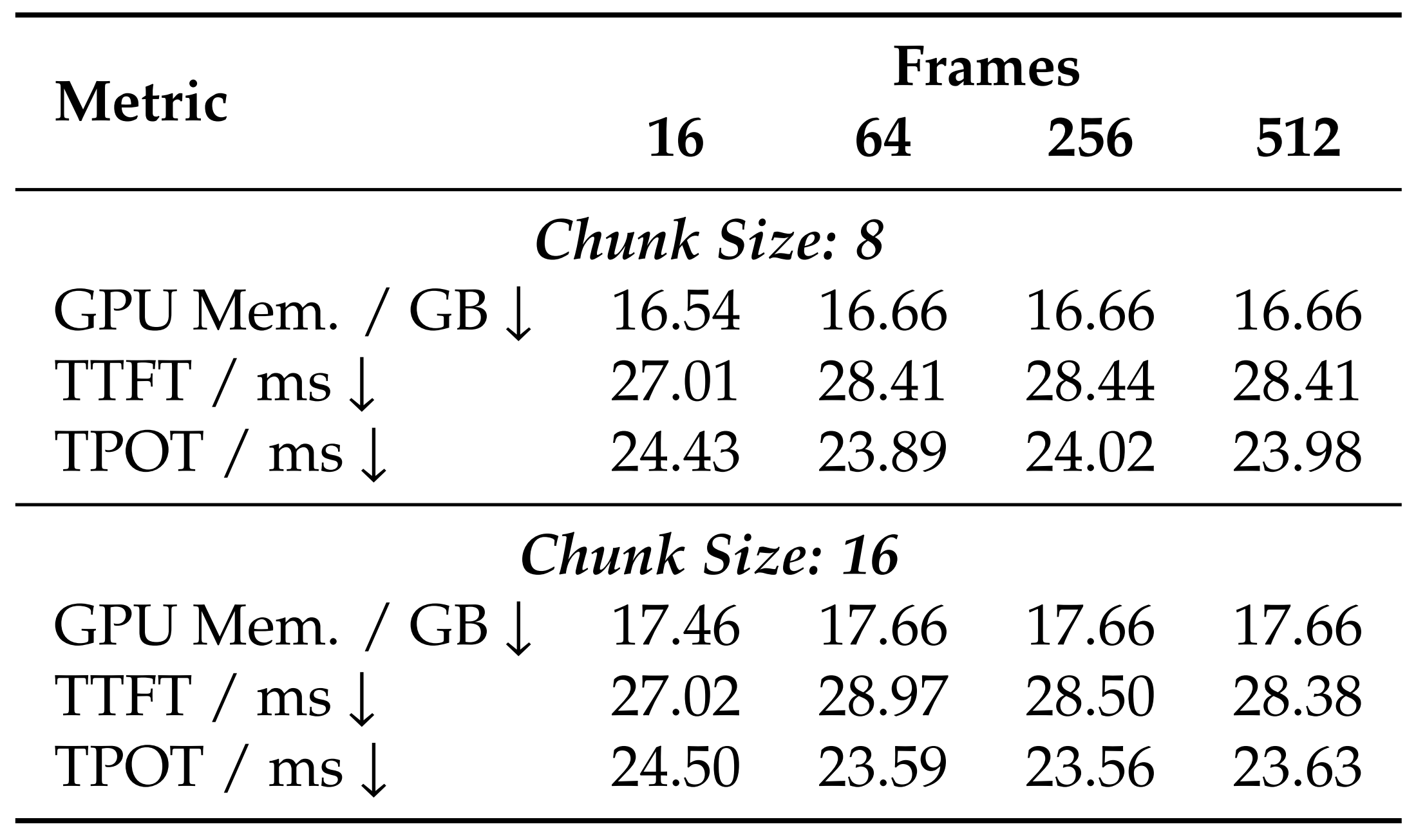
Efficiency across input frame numbers under two chunk sizes. "TTFT" denotes Time to First Token and "TPOT" denotes Time Per Output Token.
@inproceedings{
rllm-serving,
title={Reasoning Language Model Inference Serving Unveiled: An Empirical Study},
author={Li, Qi and Wu, Junpan and Liu, Xiang and Wang, Yuxin and Li, Zeyu and Tang, Zhenheng and Chen, Yuhan and Shi, Shaohuai and Chu, Xiaowen},
booktitle={The Fourteenth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2026},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=6CGjZYp6ft}
}